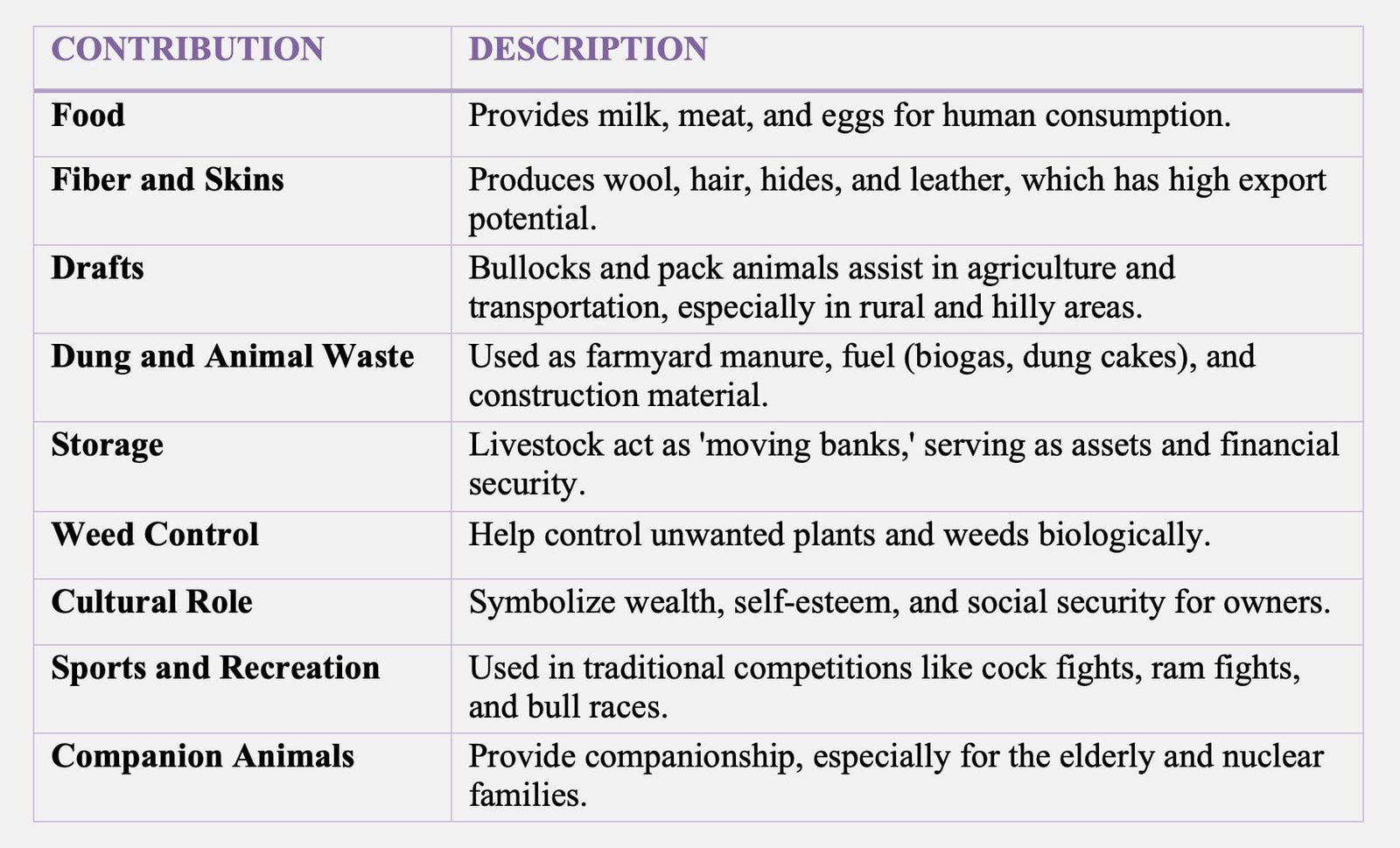
Common Terms Used in Animal Husbandry
Common terms used in animal husbandry for livestocks are:
- Abomasum: Abomasum is the forth compartment, or true stomach, of the ruminant animal
- Abort: Abort is to expel the foetus prematurely
- Afterbirth: Afterbirth is the membranes expelled after the birth of the fetus
- Animal management: Animal management is the art and science of combining ideas, facilities, processes, materials and labour to produce a market worthwhile product or service successfully. Livestock management involves integrated application of the principles of animal breeding, feeding, housing, organization and disease control in a manner suitable for a particular situation.
- Anthelmintic: Anthelmintic is a chemical compound used for treating internal worms in animals
- Antibiotic: Antibiotic is a chemical agent that prevents the growth of a germ or bacteria
- Antimicrobial: Antimicrobial is a substance that can destroy or inhibit the growth of microorganisms ie., an antimicrobial drug
- Antiseptic: Antiseptic is a substance used to kill harmful organisms on the skin surface
- Anus: Anus is the opening at the end of the large intestine that is the termination of the digestive system and through which feces pass out of the body
- Apparel wool: Apparel wool is a fine wool used in making clothing
- Arsenical: Arsenical is a drug containing arsenic
- Artificial insemination: Artificial insemination is the placing of sperm in the female reproductive tract by other than natural means
- Bitch: An adult female dog
- Boar: An adult uncastrated male pig used for breeding
- Bobby calf: A male calf about 1 week old
- Bos indicus: Bos indicus is humped cattle found in tropical countries
- Bos Taurus: Bos taurus is the domestic cattle originating from either the Aurochs or the celtic shorthorn
- Bovine: Bovine is a generic name for cattle
- Brand: Brand is a marking placed on the hide of an animal by applying extreme heat, cold, paint or caustic materials
- Breed: Breed is a group of animals with distinct shapes and colors which produce offspring with similar shapes and colors
- Breeding Bull or Stud Bull: An adult male used for breeding
- Broken-mouth: Broken-mouth is a mouth having teeth missing. Usually applied to sheep or goats and occurs with old age
- Browse: Browse is the shoots, twigs, and leaves of brush plants found growing on rangeland. Browse is a fodder obtained from eating leaves and twigs of bushes
- Buck: Buck is a male of such species as goats, deer, rabbits, etc, Buck is an intact mature, male goat
- Buck or he-goat: An adult male goat used for breeding
- Buckling: Buckling is an intact, immature male goat
- Buffalo bull calf: A male young one
- Buffalo calf: A young one of either sex
- Buffalo heifer calf: A female young one
- Bull: Bull is a male of bovine of any age that has not been castrated
- Bull calf: A male young one under 1 year of age
- Bull: Bull is an intact male bovine
- Buller: A female which is always in heat or estrus. It is also known as a nymphomanic animal.
- Bulling: Bulling describes a cow on heat or the act of service by the male
- Bullock or Steer: An adult castrated male used for carting and tillage
- Burdizzo : Burdizzo is an instrument used for bloodless castration which clamps off the tissue connecting the testis to the rest of the body
- Calf: Calf is a beef animal under one year of age, Calf is a young bovine of either sex
- Calve: Calve is to give birth to a calf
- Calving: The act of giving birth to a young one
- Calving interval: Calving interval is the length of time from one calving to the next
- Cannibalism: Cannibalism is the act of eating another member of the same species. Seen in poultry and swine
- Capon: Capon is a male chicken whose reproductive organs have been removed or rendered inactive while the individual is still young
- Caponization: A process in which the testes are removed from the adult male. This is done to make a good table bird (for eating purpose).
- Carbohydrate: Carbohydrate is a organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
- Carcass: Carcass is the dressed body of an animal or deal animal
- Carpet: Carpet wool is a coarse wool used for making carets
- Carrying capacity: Carrying capacity is the number of animals that can be grazed on a pasture during the grazing season
- Cast: Cast is to make the animal fall on the ground
- Castrate: Castrate is to remove the testes of the male or to render them inactive; alternatively, an animal whose testes have been removed or rendered inactive
- Cattle: Cattle is the animals of the family bovine, genus bos
- Chevon: Chevon is the meat from goats
- Clip: Clip is to cut hair from animals; also, the total of the wool shorn from a flock
- Colostrums: Colostrums is the milk produced the first few days after parturition
- Concentrate: Concentrate is the feed containing less than 18 percent crude fiber when dry; grains and protein supplements are concentrates
- Conception rate: Conception rate is the percentage of a group o animals that become pregnant when bred
- Corral: Corral is a small, fenced yard for confining livestock (khola, kraal)
- Cow: Cow is a female bovine that has had one or more calves; or an older female that has not had a calf but has matured
- Cow: Cow is a mature, female bovine having had at least one calf. (N.B. a cow between her first and second calves is often known as a ‘first-calf heifer’.)
- Creep: Creep is an enclosure to which only the young of the species have access so they may be fed separately from the adult stock
- Creep feed: Creep feed is used to provide special feed for the young; also, the feed provided for the young within a special enclosure
- Crisscrossing: Crisscrossing is the mating crossbred females to a sire belonging to one of the parent breeds of the female; also called backcrossing
- Crone: An old broken mouthed ewe which has been retained in a breeding flock because of her excellent breeding performance.
- Crutch: Crutch is used to remove soiled wool from between the hind legs
- Cud: Cud in ruminants, a ball-like mess of feed that is brought up from the stomach to be rechewed
- Cull: Cull is used to dispose of the poorer animals in a herd or flock
- Tagging:Tagging is the removal of soiled wool from a sheep’s hindquarters
- Dam: Dam is the mother of an animal
- Deadweight: Deadweight is the weight of an animal after it has been slaughtered and the offal, head and hide removed
- Dehorn: Dehorn is used to remove chemically or mechanically the horns of livestock
- Dewlap: Dewlap is a hanging fold of skin under the neck of animals, especially some breeds of cattle and goats
- Digestible energy (DE): Digestible energy (DE) is the gross energy of a feed minus the energy remaining in the feces of the animal after the feed is digested
- Digestible protein (DP): Digestible protein (DP) is that protein of the crude protein in a feed that can be utilized by an animal
- Disbud: Disbud is used to remove or prevent growth of the horn buds in young livestock
- Disinfectant: Disinfectant is a substance used to kill harmful organisms on non-living surfaces
- Dock: Dock is used to remove all or part of the tail
- Doe: Doe is a female of those species in which the male is called a buck; for example; goats, deer, rabbits, etc . Doe is a female goat, rabbit or antelope
- Domesticate: Domesticate is to adapt the behavior of an animal to fit the needs of people
- Double rig: Both the testicles are retained in the abdomen. It is also known as or double ridgling “Cryptorchid”
- Draft animal: Draft animal is an animal used for pulling loads
- Drench: Drench is the medicine in a liquid form administered to the animal through the mouth
- Elastrator: Elastrator is an instrument used to place strong rubber bands over, the scrotum or tail for castration or docking, respectively
- Electrolyte: Electrolyte is a solution containing salts and energy sources used to feed young animals suffering from scours (diarrhea)
- Environment: Environment is the total of the external conditions and influences that affect the life and development of living organisms
- Estrus: Estrus is the time during which the female will accept the male for copulation; also referred to as being “in heat”
- Ewe: Ewe is a female sheep or lamb ;Ewe is a mature female sheep
- Ewe lamb: A female young one
- Feed efficiency: Feed efficiency is the ratio of units of feed needed per one unit of production
- Feeder calf: Feeder calf is a weaned calf that is under one year of age and is sold to be fed for more growth
- Feeding standard: Feeding standard is a table of nutrient requirements for an animal
- Fertilization: Fertilization is the union of a sperm cell with an egg cell
- Fleece: Fleece is the total wool coat of a sheep
- Flock: Flock is a group of animals (sheep, goats, birds). (See herd)
- Flush: Flush is used increase feed level of females prior
- Flushing: Flushing increasing the amount of feed to an animal for a short period of time, usually just prior to breeding
- Free martin: When twin calves of different sexes are born the bull calf is usually sexually normal but the heifer calf is always sterile, and the external genitalia are abnormal in structure. The most widely accepted explanation being that sex hormones from the earlier developing male twin pass across to the female twin, with the result that sexual differentiation of both male and female proceeds under control of male hormones
- Gimmer: A female sheep which is between 1 and 2 shearing
- Goat: Common gender
- Goatling: A female goat over 1 year but not exceeding 2 years of age
- Grease: Grease impurities present in a fleece
- Grease mohair: Grease mohair is a mohair fleece before it is cleaned
- Grease wool: Grease wool is a wool fleece before it is cleaned
- Haylage: Haylage is the low-moisture grass silage
- He-buffalo: An adult male buffalo
- Heifer: Heifer is a female bovine that has not had a calf or has not matured as a cow
- Heifer calf: A female young one under 1 year of age
- Herbivorous: Herbivorous is the practice of eating plants as the main part of the diet
- Hermaphrodite: A bisexual animal. The word is used for animals in which the sexual organs are structurally abnormal or which possess organs simulating those of both sexes.
- Heterosis: Heterosis improvement in the offspring resulting from favorable combinations of gene pairs; some times called hybrid vigor
- Inbreeding: Inbreeding is the mating of related animals
- Kemp: Kemp is large, chalky while hairs found in the fleece of some breeds of goats, especially the Angora
- Kid: Kid is a goat under one year of age
- Kidding: The act of giving birth to a young one
- Kindling: The act of giving birth to a young one
- Lamb: Lamb is a young sheep
- Lambing: The act of giving birth to a young one
- Legume: Legume is a plant of the family leguminosae that carries its seeds in a pod that splits along its seams; many legumes have nitrogen fixing bacteria in nodules on the roots that can transform nitrogen in the air into a form(NH3) that can be used by the plant; peanuts, soybeans, clovers and alfalfa are common legumes used in agriculture
- Livestock: Livestock means stocks that are live and are used for production of items for commercial and for domestic consumption. The term livestock includes all animals, birds and all living creatures used for producing items for the use of man. The term livestock production or animal production is used to indicate farm animal production.
- Mineral: Mineral is a inorganic substance needed in small amounts for proper nutrition
- Mohair: Mohair is the fleece of the Angora goat
- Moufflons: Moufflons is a breed of wild sheep believed to be ancestors of some present-day domestic breeds
- Ovulation: Ovulation is the release of the egg cell from the ovary
- Ovum: Ovum see egg
- Palatable: Palatable is the good tasting
- Parturition: Parturition is the act of giving birth
- Pedigree: Pedigree the record of the ancestors of an animal
- Pelleting: Pelleting is the grinding a feed into small particles and then forming it into a small, hard form called a pellet
- Penis: Penis is the male reproductive organ that contains the urethra and deposits the sperm into the female reproductive tract
- Phenotype: Phenotype is the physical appearance of an animal
- Placenta: Placenta in mammals, the structure by which the fetus is nourished in the uterus
- Polled: Polled is not having horns
- Protein: Protein is an organic compound made up of amino acids and containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
- Protozoa: Protozoa is one called animals
- Puberty: Puberty is the age at which sexual maturity is reached
- Pulsator: Pulsator is a control unit used with milking equipment to control the action of the inflation in the test cup shell
- Ram: Ram is a male sheep or lamp that has not been castrated
- Ram lamb: A male young one
- Ram or Tup: An adult male sheep used for breeding
- Rectum: Rectum is the last part of the large intestine
- Rumen: Rumen is the first and largest compartment of the ruminant stomach
- Rumen organisms: Rumen organisms is a bacteria found in the rumen of cattle and other ruminant animals
- Repeatability: Repeatability in dairy cattle, a measure of the confidence that can be placed on the predicted difference being a true measure of a bull’s ability to transmit genetic characteristics
- Reproduction: Reproduction is the production of offspring
- Roughage: Roughage is a feed containing more than 18 percent crude fiber when dry; examples, hay, silage, and pasture
- Ruminant: Ruminant is an animal that has a stomach divided into several compartments; for example, cattle, sheep, goats
- Rumination: Rumination in ruminants, the process of chewing the cud
- Scrotum: Scrotum is the saclike part of the male reproductive system outside the body cavity that contains the testicles and the epididymis
- Seggy: A ram castrated after service.
- Semen: Semen is the mixture of the seminal and prostate fluid and the sperm
- Shearing: Removal of wool
- She-buffalo: An adult female buffalo
- Slink calf: An aborted calf
- Staple: Staple is a fiber of materials such as wool, cotton, or flax, either in its natural state or after it has been carded or combed; also refers to the length, fineness, condition, or grade of the fiber
- Steer: Steer is a male bovine animal that was castrated before reaching sexual maturity
- Store cattle: They are meant for beef production and more commonly known as the cattle fed for butchers
- Tagging: Tagging is shearing a ewe around the udder, between the legs, and around the dock; also called crutching
- Teat: Teat is the outlet for milk produced in the udder
- Testicles: Testicles is the male organs that produce the sperm cells
- Testosterone: Testosterone is the male hormone that controls the traits of the male animal
- Udder: Udder is the milk producing gland of mammals such as cows
- Urea: Urea is a synthetic nitrogen source that is manufactured from air, water, and carbon
- Urine: Urine is the liquid waste collected in the bladder
- Uterus: Uterus is the part of the female reproductive system where the fetus grows; also called the womb
- Veal: Veal is the calves younger than three months of age sold for slaughter
- Vitamin: Vitamin is an organic compound needed in small amounts for nutrition
- Wattle: Wattle is a projection of skin hanging from the chin or throat, especially in poultry and some breeds of goats
- Wedder or Wether: An adult castrated male sheep.
- Wether: Wether is a male sheep or goat that has been castrated before reaching sexual maturity
- Yearling: A horse over 1 year and under 2 years of age
- Yearling bull: An uncastrated male between one and two years
- Yeld or Eild: A barren or non lactating animal